Ayutthaya Kingdom Open: The fall of the former Past Empire
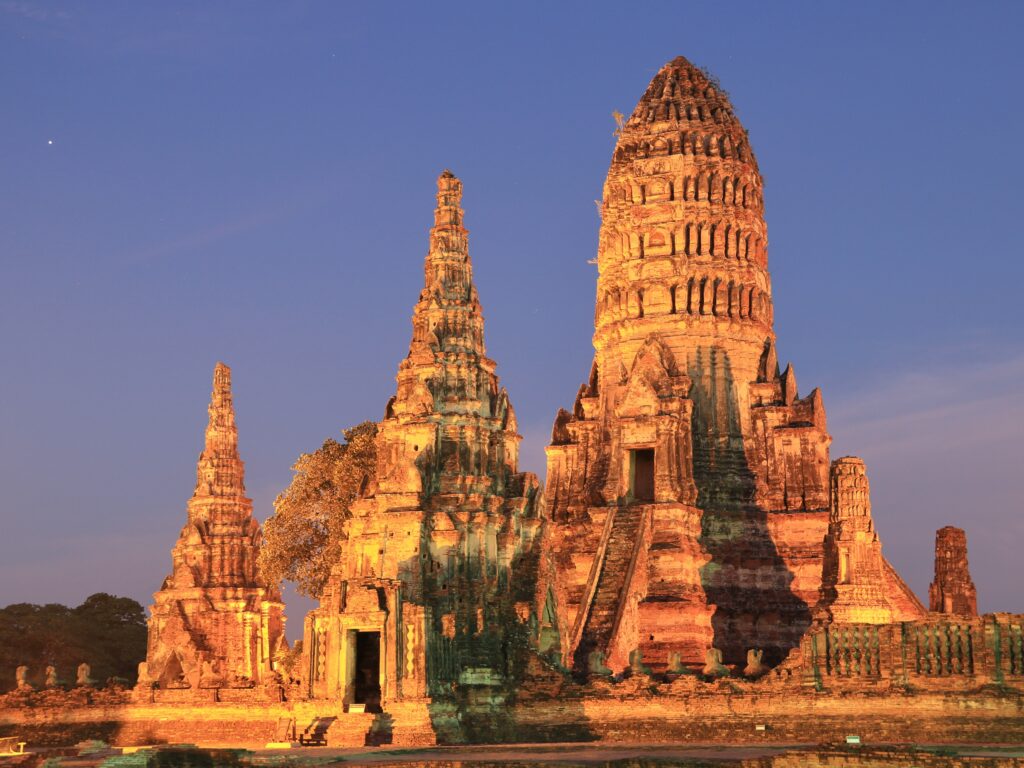


Ayuttha’s rise
Ayutthaya’s Empire, a powerful and prosperous Siam Kingdom located in Southeast Asia in many areas such as the kingdom or culture, trade and military power of Ayutthaya. Royal Ramathibodi I set up in 1351 and became one of the super powers in Asia quickly.

Chao Phraya, Lopburi and PA, with a strategic location near the rivers of the royal, the Kingdom has allowed the kingdom to manage trade roads between the Indian and Malay Peninsula. During the pijnik, the Kingdom became one of the superpowers in Asia.
Many European traders and diplomats were impressed by the width and greatness of the capital. Some travelers compared this city for other European cities such as Paris and Venice. Many visitors described the wealth, gold palace, giant fortresses and elegant teak houses (Harrington, 2004) in a city full of golden teacks. Strong diplomatic relations, a giant military and economic power, Ayutthaya successfully kept their neighboring rivals successfully attacking the kingdoms for the next centuries.
Burmese Siam’s occupation
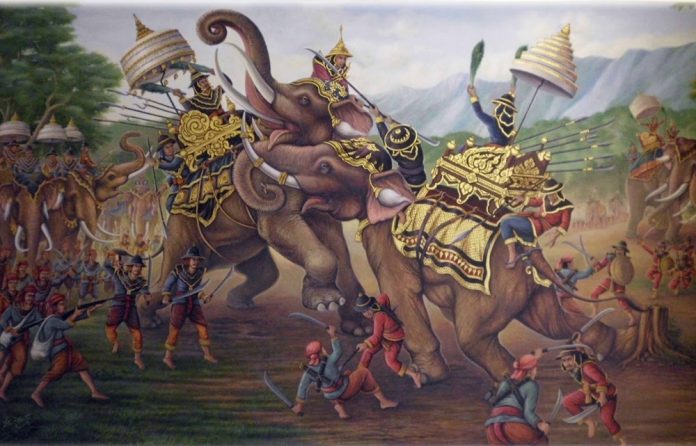

Peace did not last long along the kingdom of Ayutthaya. The competition between the Burma and the Siam Kingdom has been available for hundreds of years. Both powers, territories, trade paths and the regional influence in the Southeast Asia region competed.
Several warfare between Siam and Burma, occurred with ineffective results since the 16th century. In 1569, King Bayinnaung successfully conquered Ayutthaya and made the Vassal State of the Kingdom Band. However, the famous Siam’s king called Nong Sarai after the Nong Sarai war, called the Great LED Siam.
After gained independence in 170 years later, King Hsinbyush rose to the Burma in 1763. The new king was ambitious and aggressive and was intended to expand the territory of Birman. After successful military campaigns in Manipur and China, King Hsinbyushin drew attention to the Kingdom of Siam.
In 1765, the royal Hsinbyushi army divided into 2 routes, northern and southern routes. These 2 sections have launched a mass and coordinated attack on Ayutthaya. The northern unit successfully conquered Chiang Mai and other northern Siam districts. On the other hand, the Southern Section, the Malay Peninsula and the territories of the Southern and conquered areas along the Gulf of Thailand.
Last siege in 1767
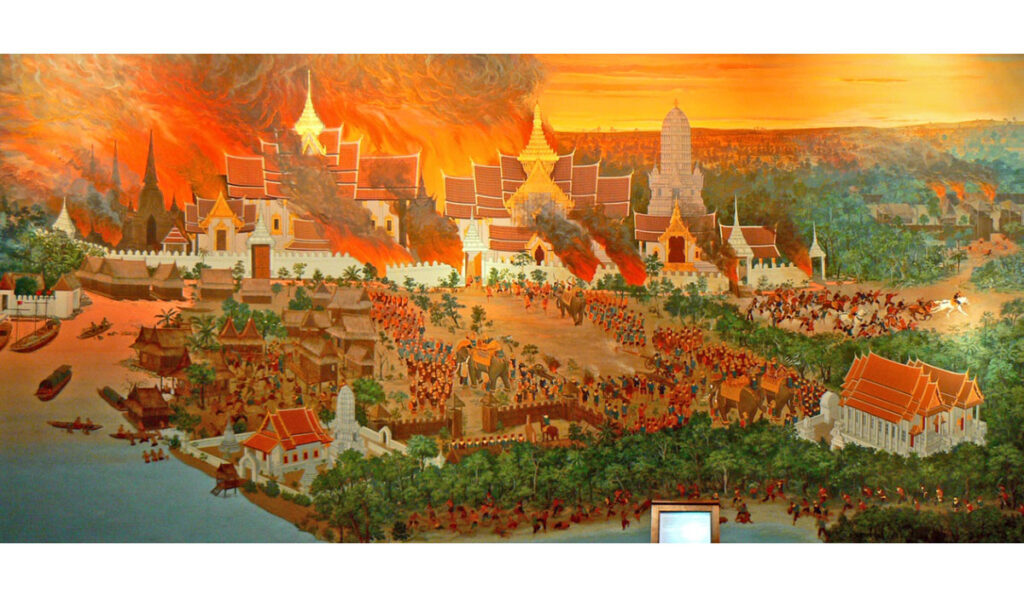

2 sections of the Burma Army finally came together in the city of Ayutthaya and united. Finally, the Burma started the final siege and the latest attacks in 1766. Burmese siamese cut the Siamese route and isolated from the capital of rural areas. On the contrary, Siamese used the traditional defense strategy by trusting only the castles and walls.
The strategy implemented by the Burma was proven successful. Ayutthaya’s population endured severe food shortages and famines. With the low supply of food and mood, the protection of the city was exhausted. During the siege, the Burmese built three forts around Ayutthaya at a heel of about 4.5 meters. The 3 castles used by the Burmese, used to bore and protect the tunnel to penetrate the city of Ayutthaya.
To oppose this castle, the Siamise army has initiated this newly built castles. King Ekkathat sent ten thousand people to close a burma castles on the packaged lines. Simase forces used portable stairs to climb Burma castles and successfully access the castles. Although he imitates his early success and castles, the Burmese reinforcements came in time and this great Siame attack. Later, these attackers returned to Ayutthaya Citadel for the rally.
Finally, on April 7, 1767, Burma violated the protection of Ayutthaya. Siam defenders could not trap disciplined Burma Army. Burmese used a newly built tunnel to open fire on Ayutthaya’s wall. The northeastern parts of the wall collapsed in the morning, and Burma entered the Burmese, Burmese Ayutthayan Citadel. The remaining forces of the 10,000 Siam defender did the last stands in Citadel, but attempts were in vain.
After the war and the fall of the kingdom of Ayutthaya
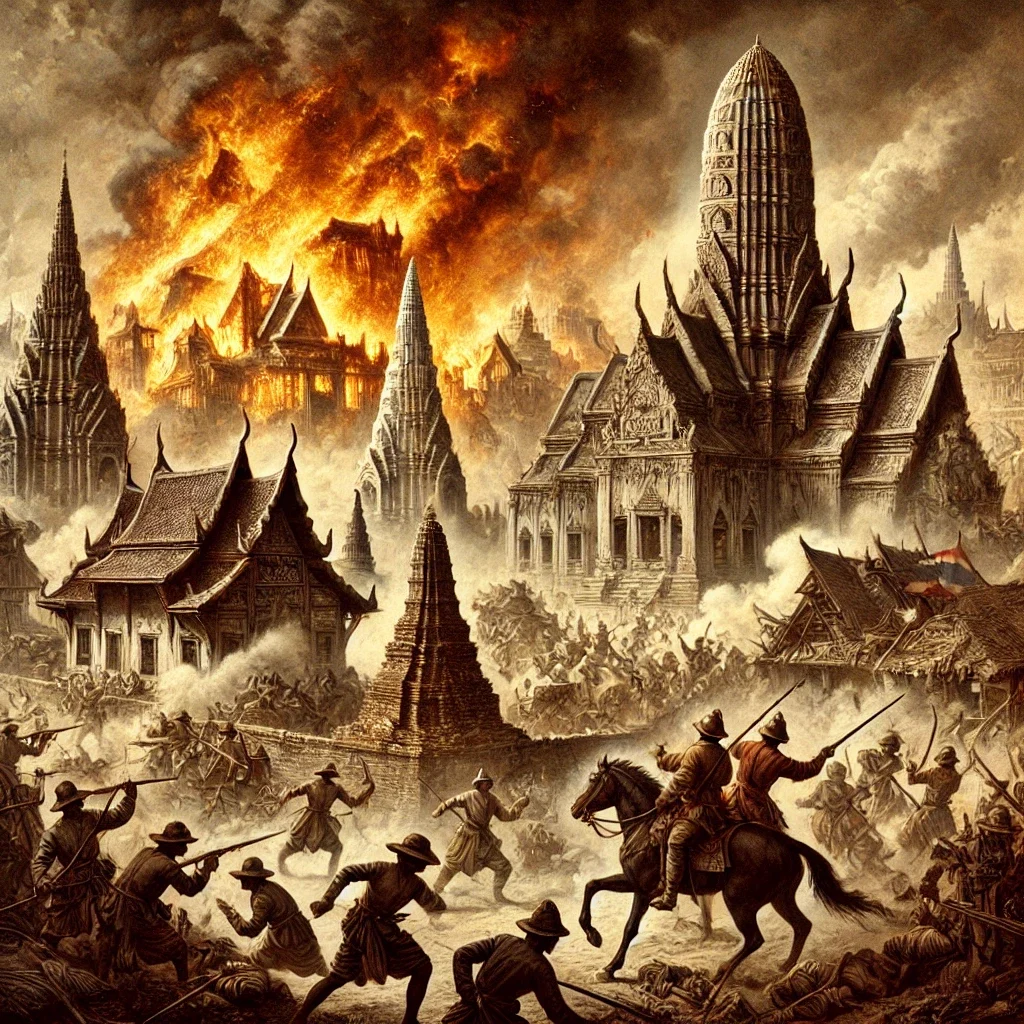
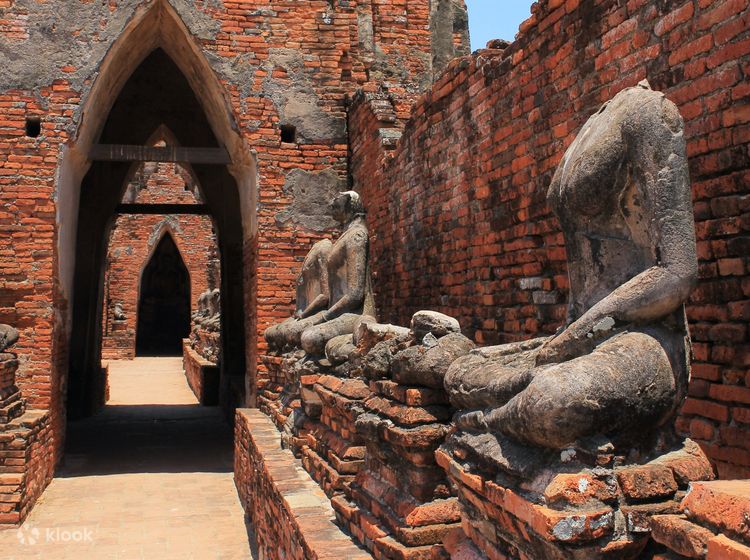


Burma carried out a burnt land tactics in Ayutthaya. The attackers killed Ayutthaya citizens they encountered on their ways. The city was completely destroyed by the city, known as the city, palace, temples and treasures, alive and wealthy.
Burmese armies set fire to many buildings, including the royal palaces and many temples. In addition, the Burma plundered many of the treasures of Ayutthaya and returned them to Myanmar. The scale of the wreck was large and was deleted from the capital of the capital.
According to some witnesses, the king of Ayutthaya tried to escape from the Ekkathat Palace to the Western gate. However, a random weapon from a burmez killed while trying to escape the city. In addition, the Burmese captured nobles, including many Siamese members and important ministers. A total of 2000 Siam Elite was seized and deported from a dropped city. Siamous wealth, such as stones, gold, Buddhist books and acts, were also taken by the conquestors.
Ayutthaya’s inheritance and the impact of the influence of modern Thailand



Despite the mass destruction of the city, Ayutthaya’s legacy survived. The city’s autumn was a turning point in the history of Thailand. The kingdom of Ayutthaya also laid the foundation of the modern Thailand. In addition, the destruction of the city shows the stability of the Thai people that can save from destruction.
The Kingdom of Ayutthaya had an important and sustainable impact on modern Thai, which forms a modern Thai, culture, politics, religion and personality. Ayutthaya has established a tradition of monarchy that lasts so far. The belief in the divine and immunity of the king continues to affect the modern Thai.
As for the religion and culture, Ayutthaya has spent and applied Buddhism in Theravada and turned to the Buddhist Learning Center. Buddhism remains the main religion of a modern Thailand that shapes the country’s identity and culture. In addition, many of Thailand’s literary works, royal traditions, art and kitchens have returned to Ayutthaya.
The last important factor is clear in the national identity of Thailand. After the conquest of Ayutthaya, I set Burma Rama, Chakri dynasty and chose Bangkok as a new capital. Bangkok successfully connected Bangkok to the political and cultural values of Ayutthaya, which ensures the protection of the national identity of Thailand.
References
https://www.renown-travel.com/historicalsites/ayutthaya/history.html
https://visitworldheritage.com/en/buddha/htoric-city-of-ayutthaya/0b451a5d-b923-4858-B7DE-74C30C301B
Harrington, Jane Therese (2004) ‘Here’: heritage, affiliation and accommodation: Avenebury (England), Magnetic Island (Australia) and Ayutthaya (Thailand) and identity formation. PhD thesis, James Cook University.
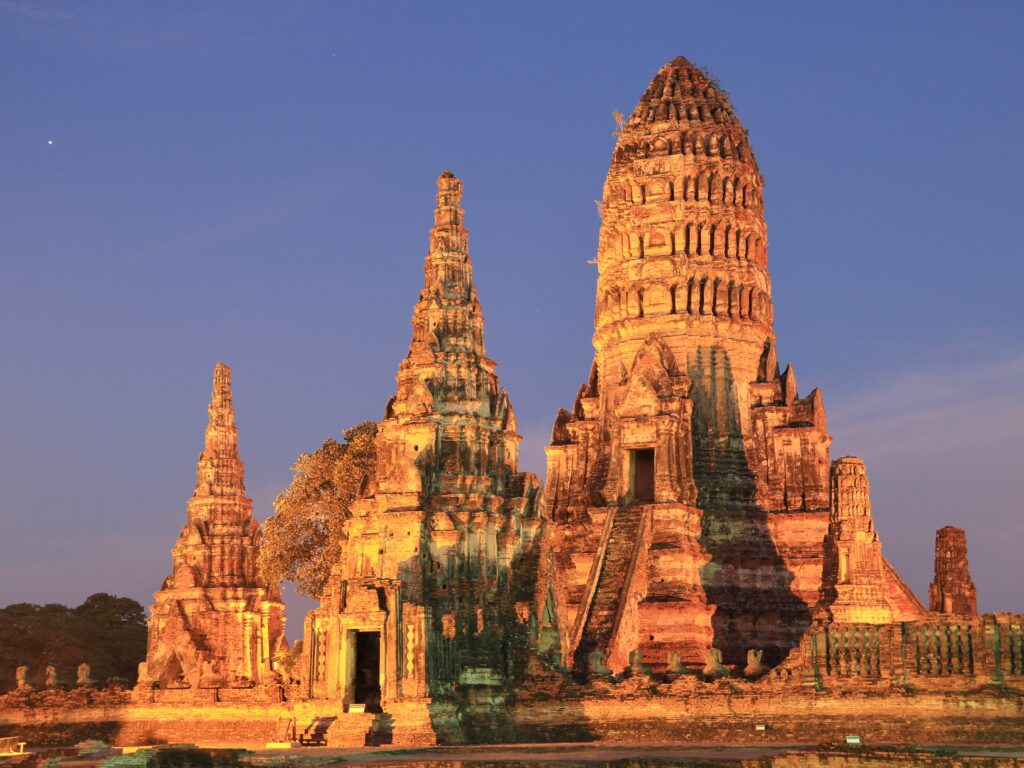













Leave feedback about this