Manila By Ages: Timeline of Asia’s Pearl of the Orient
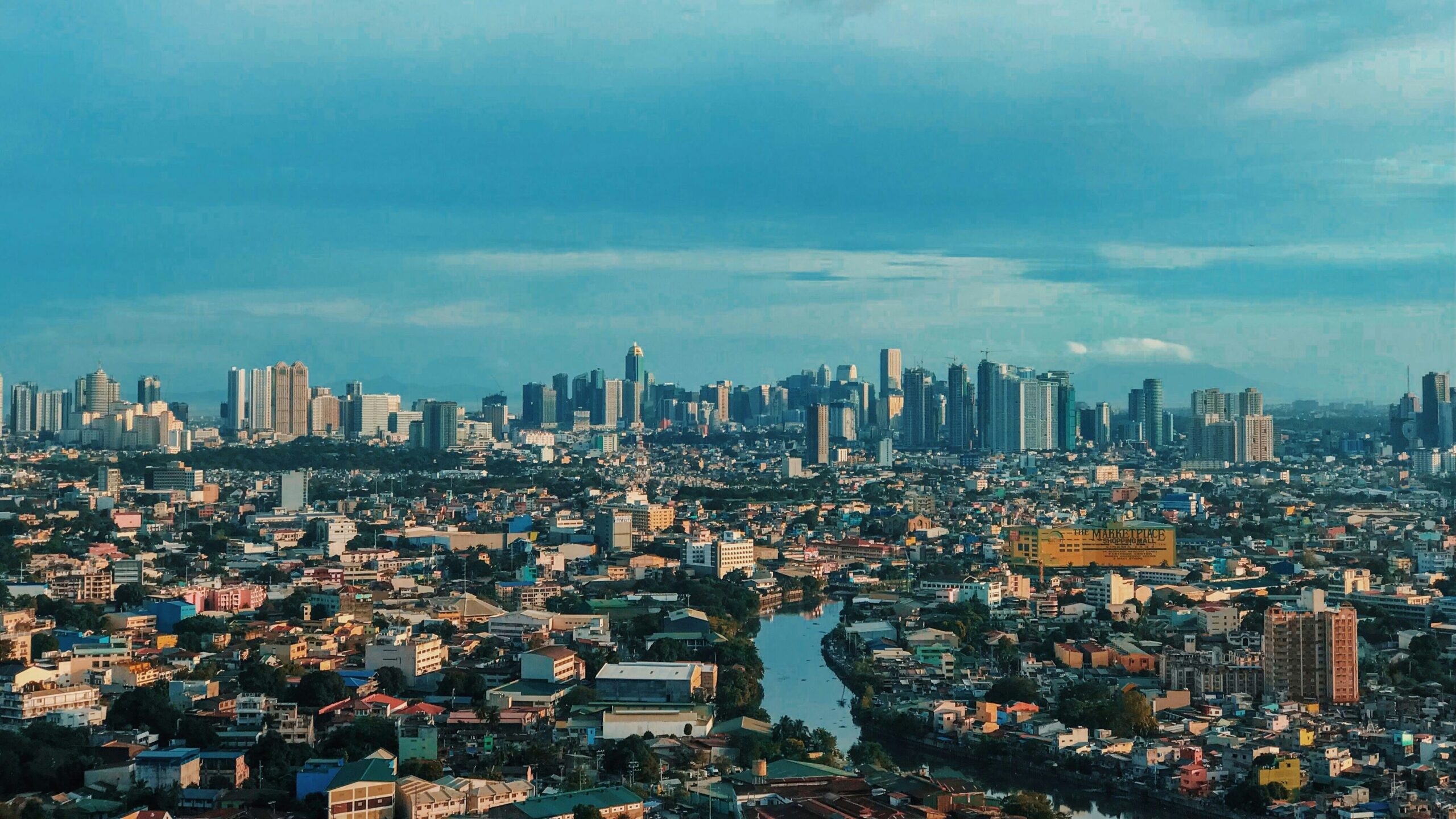

Manila metropolis, the capital of the Philippines, identified by many because the Pearl of the Orient. The given title displays the town’s achievement for its historic significance, wealthy cultural heritage, financial powerhouse, and strategic place in Asia. Manila began as thriving pre-colonial settlement to its transformation into a contemporary metropolis. Town possess fascinating story of resilience, conquests, and rebirth.
Manila throughout pre-colonial period
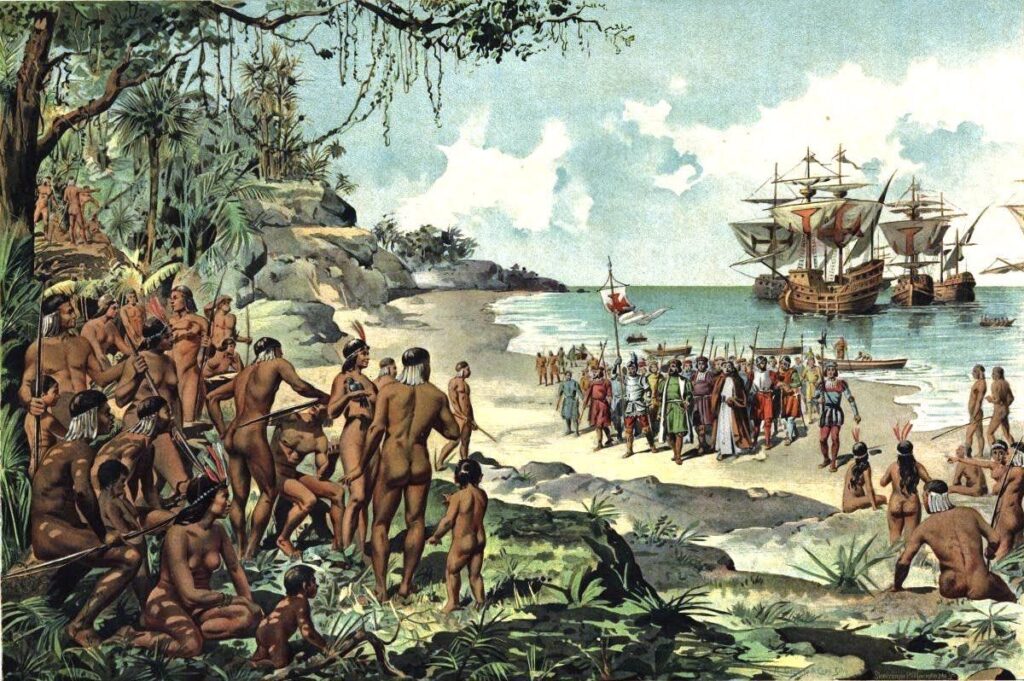

Earlier than the Spanish colonization, Manila already turned a thriving settlement as a result of its strategic location. Located alongside the banks of Pasig river, it turned the house to the Rajahnate of Maynila and serves as a serious commerce hub in Luzon.
Throughout this time period, the town of Maynila possess a robust commerce relation with neighboring Southeast Asian nations, in addition to retailers from China, India, and the Center East. The individuals of Manila primarily Tagalos, lived in organized barangays. Furthermore, they enganged in agriculture, fishing, and craftmanship.
With its fortified settlements, bustling marketplaces, and wealthy mix of indigenous and overseas influences, pre-colonial Manila turn into a testomony and a robust proof to the Philippines’ deep-rooted historical past lengthy earlier than the Spanish arrival.
Manila after the Spanish Conquest
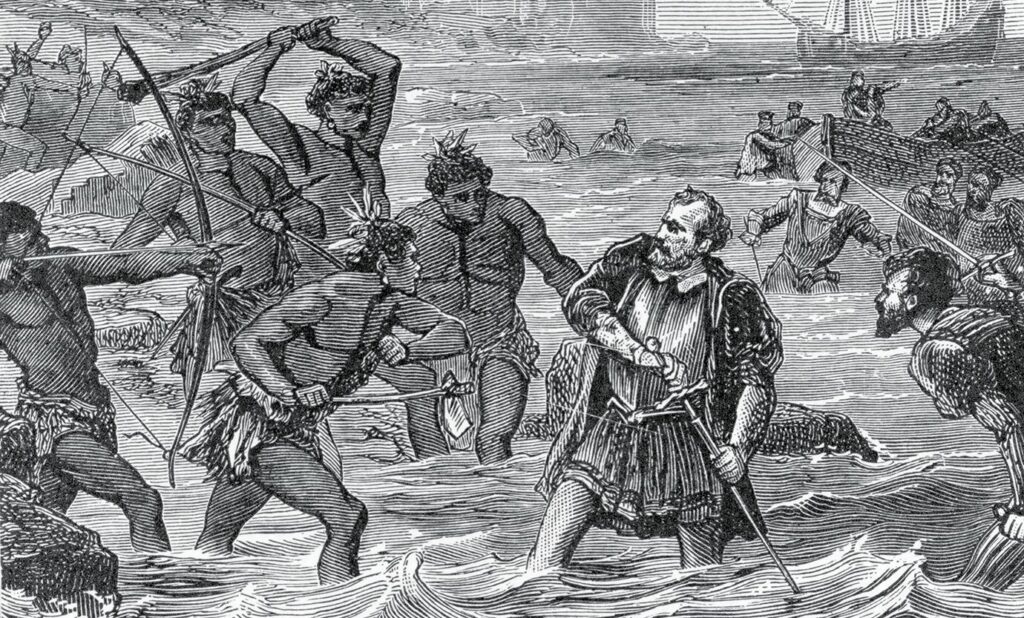


Governor-Basic Miguel Lopez de Legazpi, looking out a brand new appropriate place to ascertain a brand new colonial capital after being attacked by Portuguese pirates. He heard a affluent kingdom of Luzon and despatched an expedition underneath Marshal Martin de Goiti and Captain Juan de Salcedo.
The Spanish forces engaged in battles towards the native rulers, together with Rajah Sulayman, Rajah Matanda, and Rajah Lakandula. Initially, the native kingdoms efficiently repelled the Spaniards, however they returned in 1571 and defeated the native forces.
After institution of the Spanish rule in Luzon, Legazpi declared Manila the Capital of Spanish East Indies (Las Islas Filipinas). Legazpi selected Manila because the capital as a result of its strategic location on Manila bay and quick access to maritime commerce routes.
Spanish Colonial Period and the Institution of Intramuros
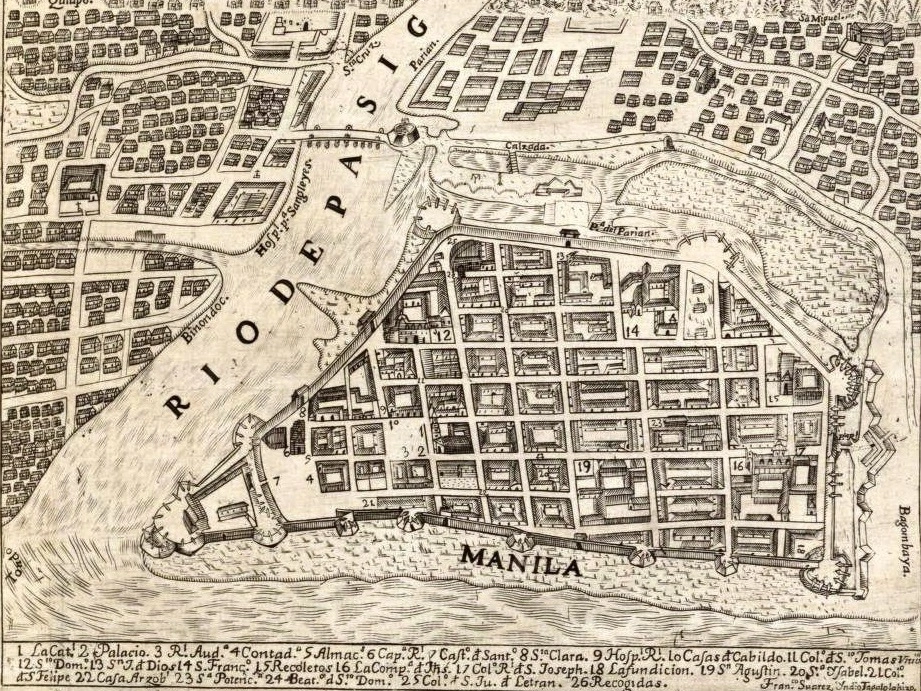
Underneath the management of Martin de Goiti, the Spaniards established the well-known intramuros, a walled metropolis that served because the political and non secular middle of the colony, on the ruins of the deserted fortress of Rajah Soliman.
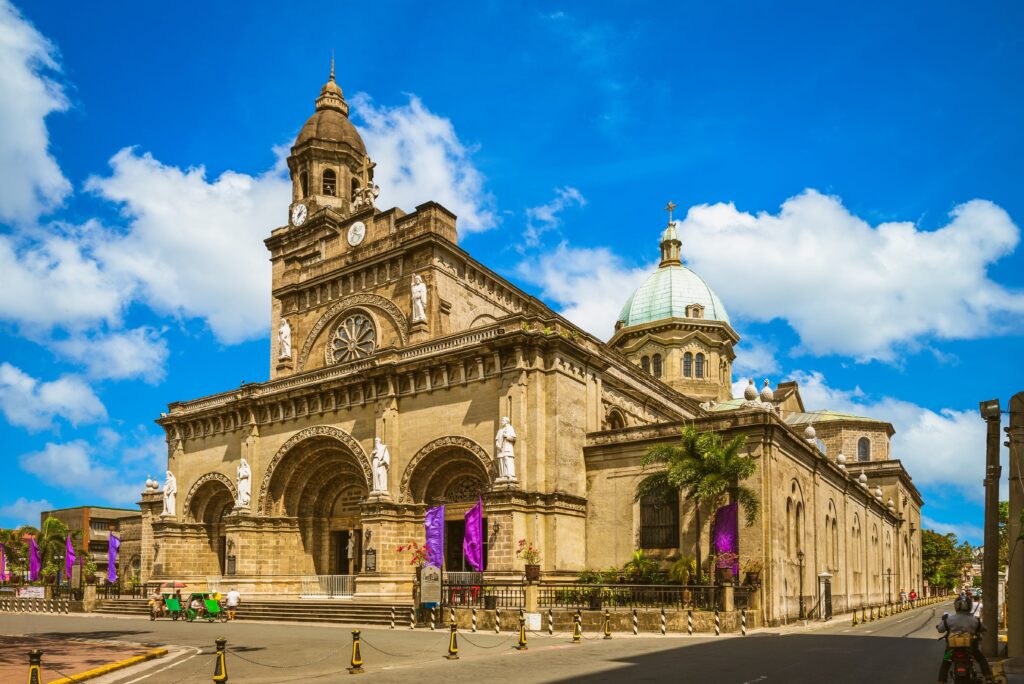
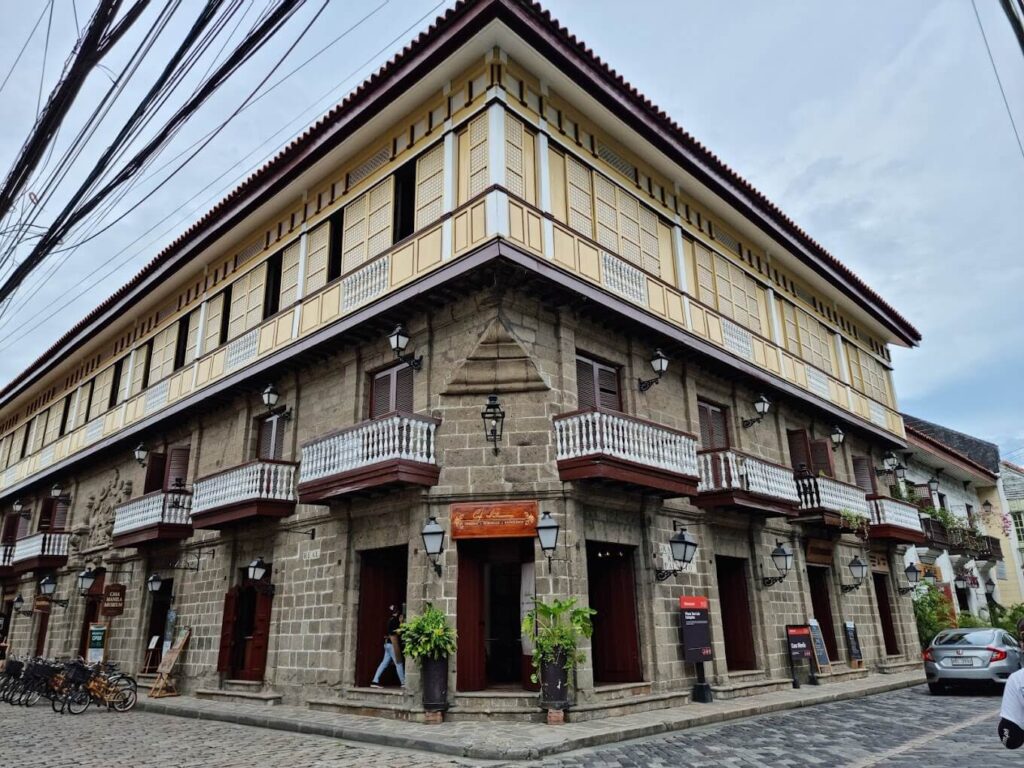
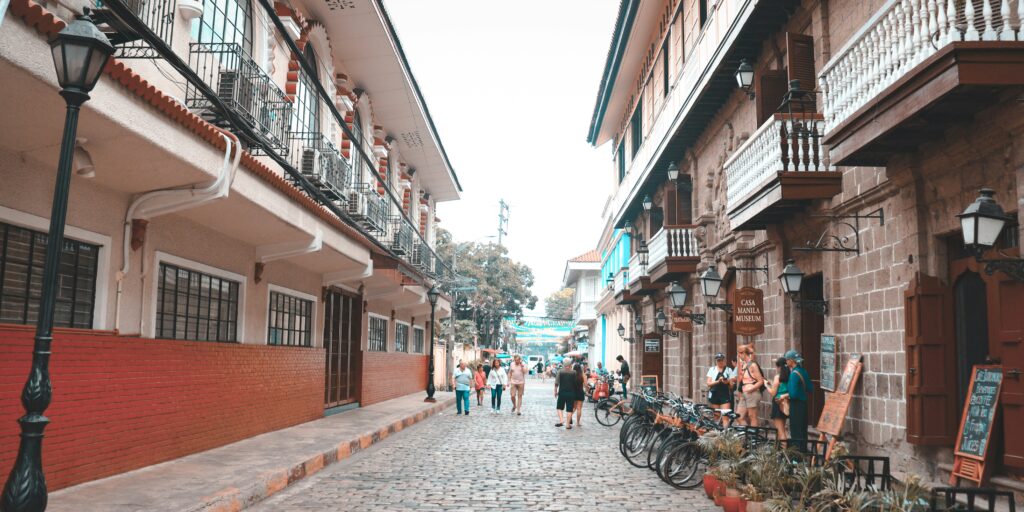






The brand new colonial metropolis was constructed following King Philip II’s Legal guidelines of the Indies, which mandated a grid format with slim streets for shade, central plazas anchoring church buildings and authorities buildings, and all constructions enclosed inside the walled fortress of Intramuros (Santos, 2022).
Additionally, throughout this era, the Spanish constructed key landmarks of Intramuros. A few of these landmarks acquired a UNESCO world heritage for its wealthy historical past and uniqueness. Key landmarks included:
- Fort Santiago: a historic fortress constructed as a army protection construction, later used as a jail and have become the place of execution of Jose Rizal
- San Augustin Church: The oldest stone church within the Philippines (in-built 1607) and a UNESCO world heritage website.
- Manila Cathedral: turned the image of catholic affect within the Philippines.
- Plaza de Roma: central plaza of intramuros, traditionally used for civic and non secular gatherings.
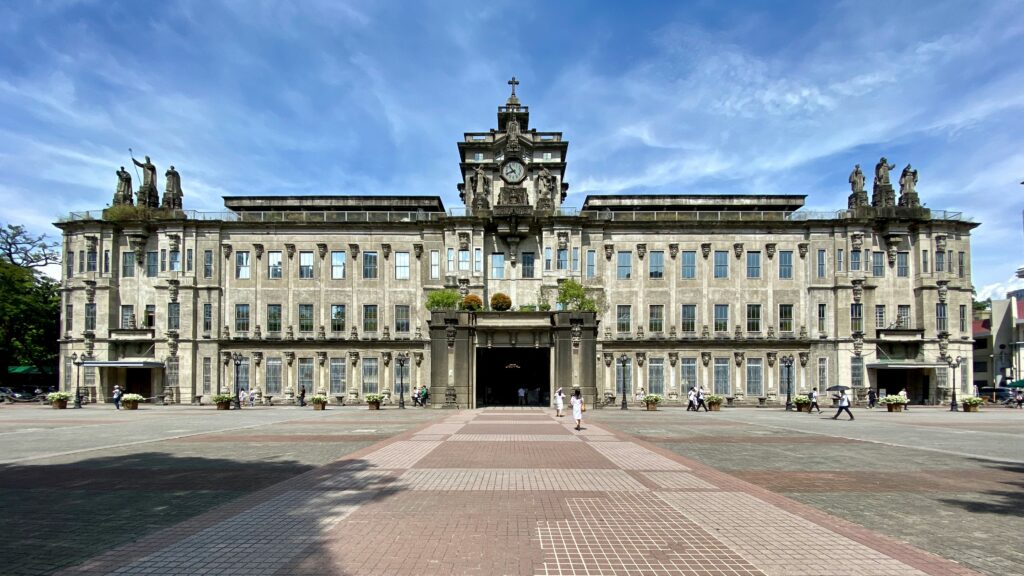
- College of Santo Tomas: Based in 1611, the oldest current college in Asia.
- Casa Manila: A reconstructed Spanish colonial home that showcases life-style of prosperous Filipinos throughout Spanish rule.
Manila as a World Commerce Hub: Manila-Acapulco Galleon Commerce (1571-1815)
Manila-Acapulco galleon commerce turned essentially the most vital side of the Spanish rule, this commerce route related Philippines, Mexico and Spain. The strategic location of Manila allowed it facilitate the alternate of Asian luxurious items, equivalent to Chinese language silk and porcelain, Indonesian spices, and Indian textiles.
In return, the Mexican silver-which turned the usual forex in Manila-and European items have been dropped at the Philippines. This commerce route made Manila one the wealthiest cities within the area, attracting Chinese language, Indian, and Arabian retailers to the town.
Manila turned a melting pot of Filipino, Spanish, Chinese language, and Mexican cultures, shaping its structure, delicacies, and traditions. The rising Sangley (Chinese language) inhabitants led to the institution of Parián, a district for Chinese language retailers and merchants, additional solidifying Manila’s function as a worldwide buying and selling middle.
Nonetheless, the commerce ultimately resulted in 1815 when Mexico gained independence from Spain, slicing Manila off from Acapulco. This compelled the town to shift in direction of an open economic system, paving the best way for its integration into international markets past Spanish rule.
Additional City Improvement of Manila underneath Spanish Rule (1815-1898)
Manila underwent vital adjustments, shifting from closed colonial port to a rising city middle. The Spanish administration began to modernizing the town, setting up new infrastructure, public buildings, and transportation networks to accommodate the individuals. Building throughout this era expanded past the walled metropolis of Intramuros, with new districts emerged to accommodate the inhabitants.
City Enlargement and Infrastructure
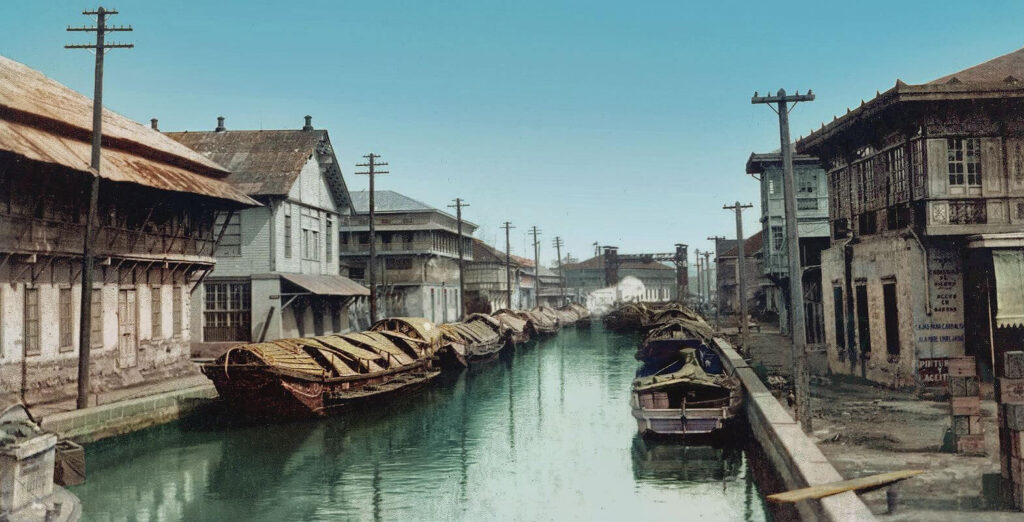


The Spanish authorities improved highway networks, linking Manila to close by provinces, facilitating the motion of products and folks. The Puente de España (Bridge of Spain), accomplished within the early nineteenth century, related Binondo and Intramuros, turning into an important commerce hyperlink between Manila’s industrial and administrative facilities. Different bridges, equivalent to Puente Colgante (Hanging Bridge), have been later added to reinforce connectivity.
To enhance sanitation and public well being, Spanish authorities constructed the Estero de Binondo and different canals, which helped regulate water circulation and forestall flooding. The Carriedo Waterworks, accomplished in 1882, supplied Manila with its first fashionable water provide system, enhancing public hygiene and lowering the unfold of illnesses.
Spiritual and Public Buildings
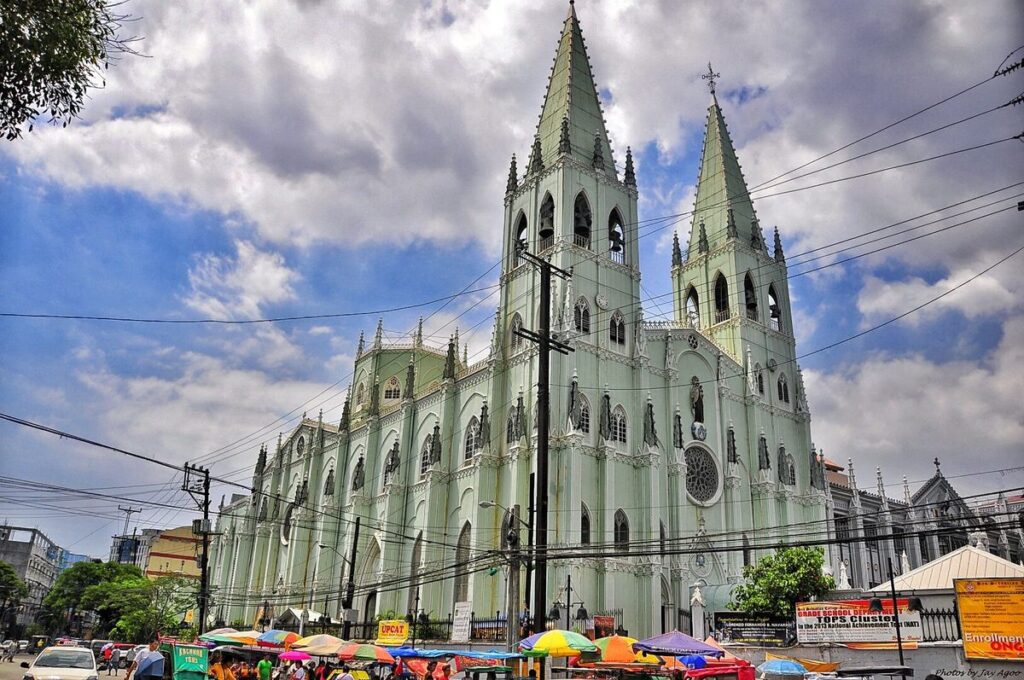


Building of church buildings remained central to Manila’s growth. The Spanish constructed the primary all-steel church in Asia, known as the San Sebastian Basilica in 1891. The metal construction designed by the Spanish to face up to earthquakes and different pure disasters.
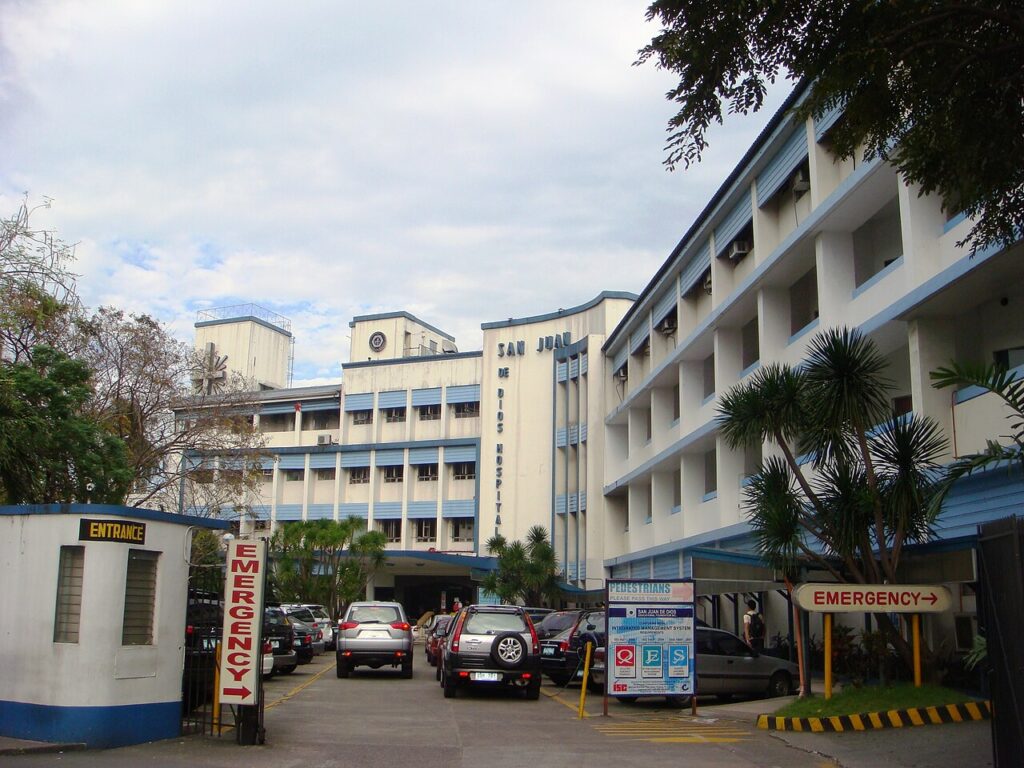
Additionally throughout this era, the Spanish authorities constructed a number of instructional establishments equivalent to Ateneo Municipal de Manila (based in 1859) and Escuela Regular Superior (1865). These colleges educated lecturers to educated the rising inhabitants of Manila. The Spanish authorities additionally modernized San Juan de Dios hospital to supply higher medical care to the civilians.
Financial and Industrial Development
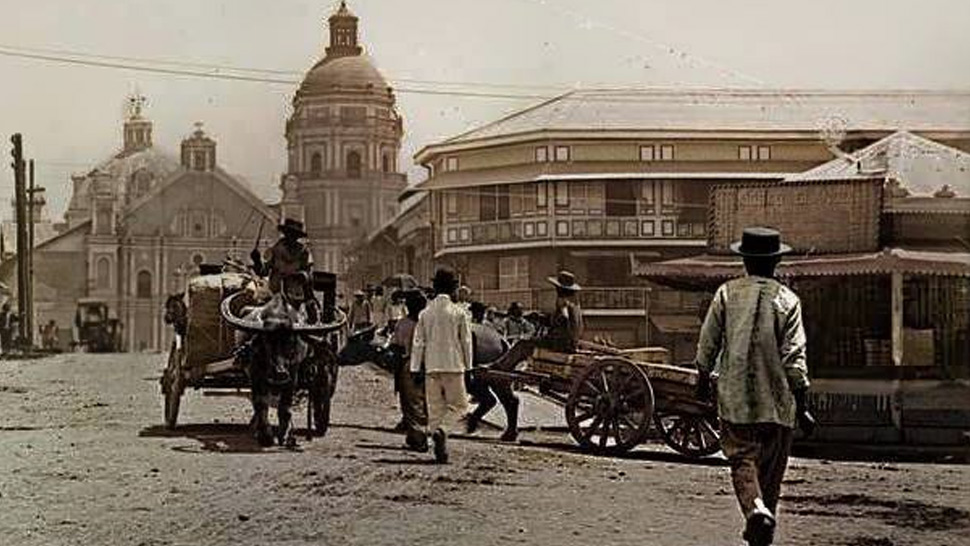

With the opening of Manila to worldwide commerce, industrial exercise shifted to Binondo, which turned Manila’s monetary district. Beforehand, established for Chinese language retailers, Binondo turned the hub of banking , enterprise, and commerce. Many factories producing tobacco, sugar, and abaca flourished on this space.
To assist Manila’s large financial growth, the Spanish authorities constructed the Manila-Dagupan railway in 1892, marking the primary railway system within the Philippines. It related Manila to agriculture areas in Central Luzon, permitting quicker transport of products to capital. The development of Port of Manila that embody growth of docking amenities, additionally assist to spice up commerce exercise within the area.
Manila throughout The Philippine revolution (1896-1898)
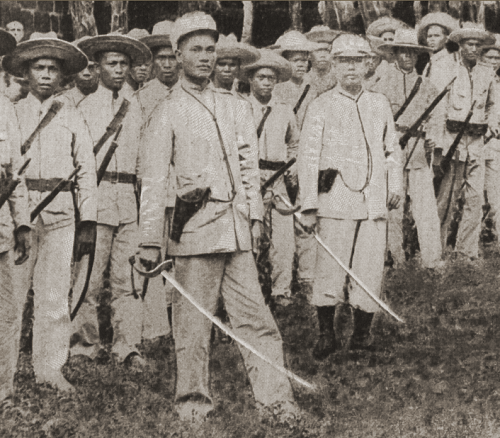

Through the Philippine revolution, led by Katipunan underneath Andres Bonifacio and Emilio Aguinaldo, Manila turned the middle of Spanish administration and army energy. The Spanish applied strict rule that limits any revolutionary actions inside the metropolis.
Throughout this time, the execution of Jose Rizal occured in 1896 at Bagumbayan (now Luneta) and fueled additional nationalist sentiment. The Spaniards strengthened Manila’s protection, together with Fort Santiago and Intramuros, as rebel unfold by way of the Phillipines.
Battles between the Katipunan and Spaniards erupted in close by provinces like Cavite and Bulacan, whereas Manila remained a contested zone. Additionally throughout this time, disruption occured in commerce and commerce, affecting Manila’s function as a worldwide commerce hub.
Manila underneath American Rule (1898-1946)
Following Spain’s defeat within the Spanish-American battle, the USA took over the Philippines by way of the Treaty of Paris in 1898. Manila noticed large adjustments in city planning and modernization throughout the American interval. The Burnham Plan of 1905, designed by American architect Daniel Burham with the purpose to modernize Manila (Santos, 2022).
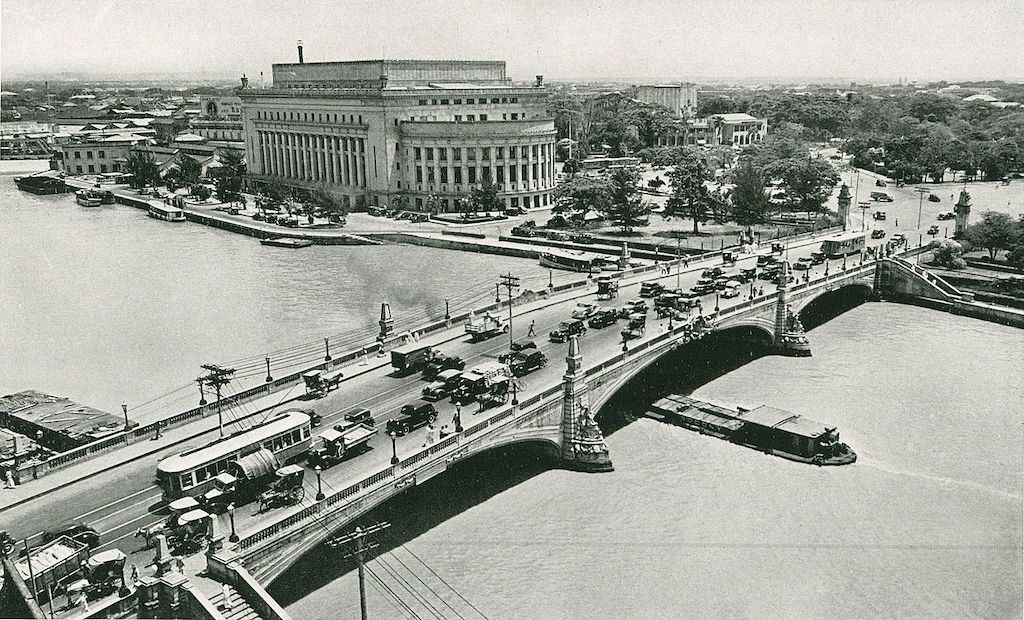
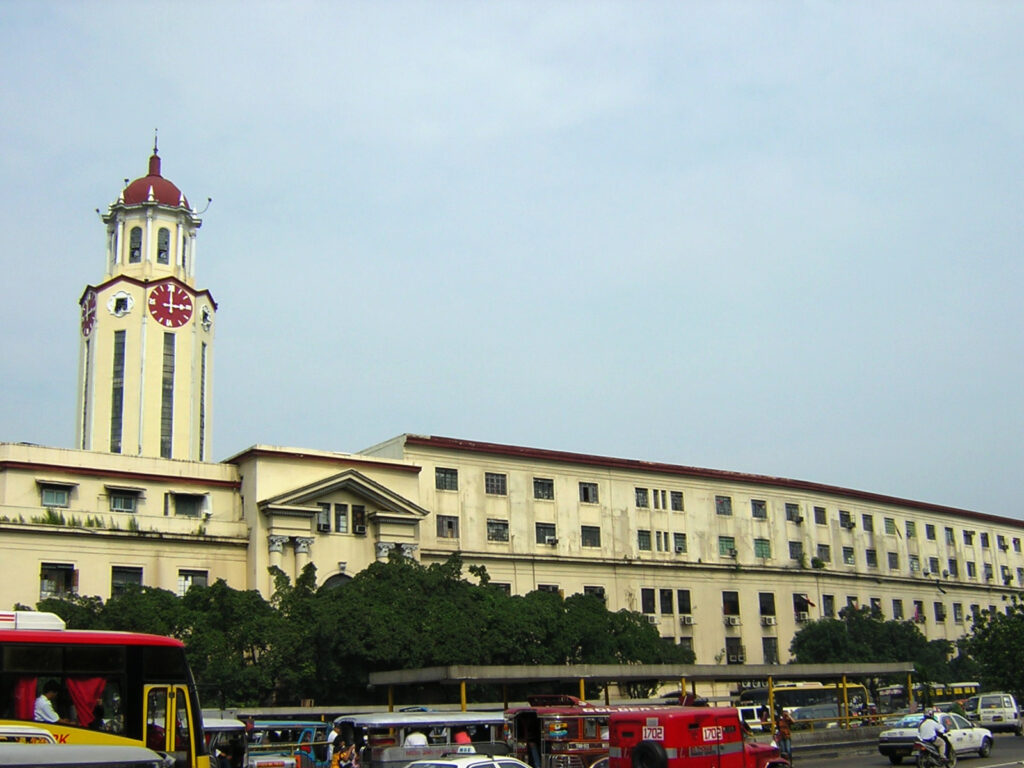
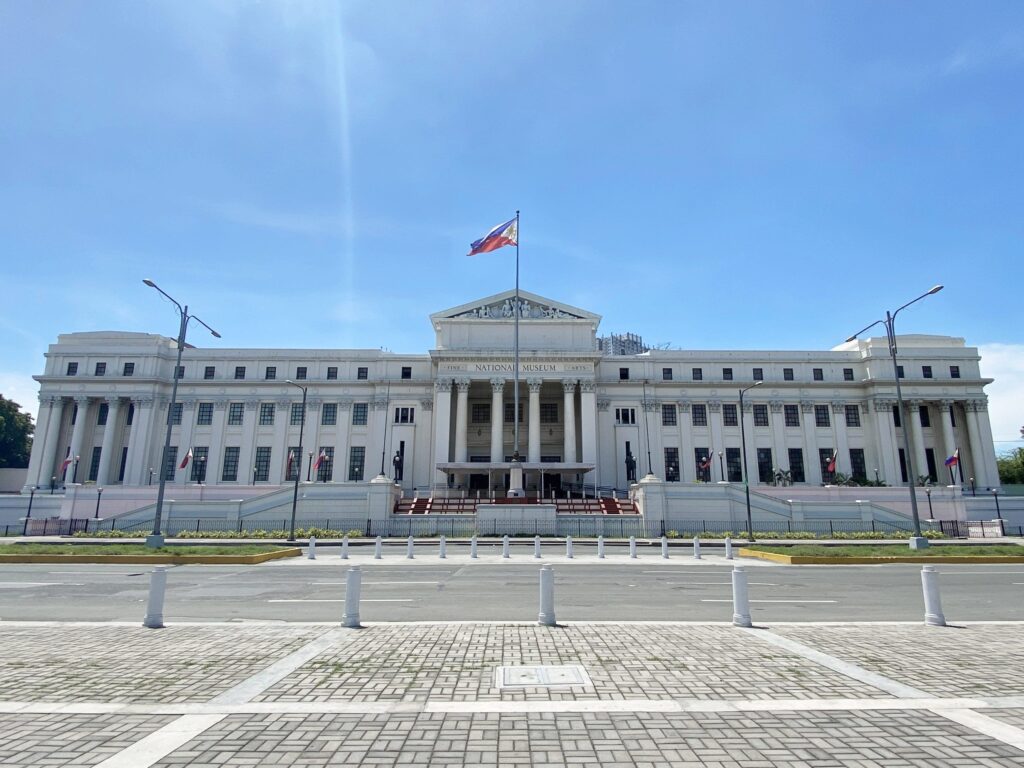




The plan applied new city planning with organized metropolis format, broad roads, parks, and neoclassical authorities buildings. The American constructed Main avenue like Roxas Boulevard (then Dewey Boulevard) and Jones Bridge to enhance Manila’s transportation entry. Moreover, additionally they established new authorities buildings just like the Manila Metropolis Corridor and the Legislative Constructing.
The People additionally launched fashionable sanitation and public well being packages, which embody sewerage system and water provide. This new amenities additionally cut back unfold of illnesses like cholera and malaria. The People additionally established new hospital like Philippine Basic Hospital (PGH) to supply fashionable healthcare providers.
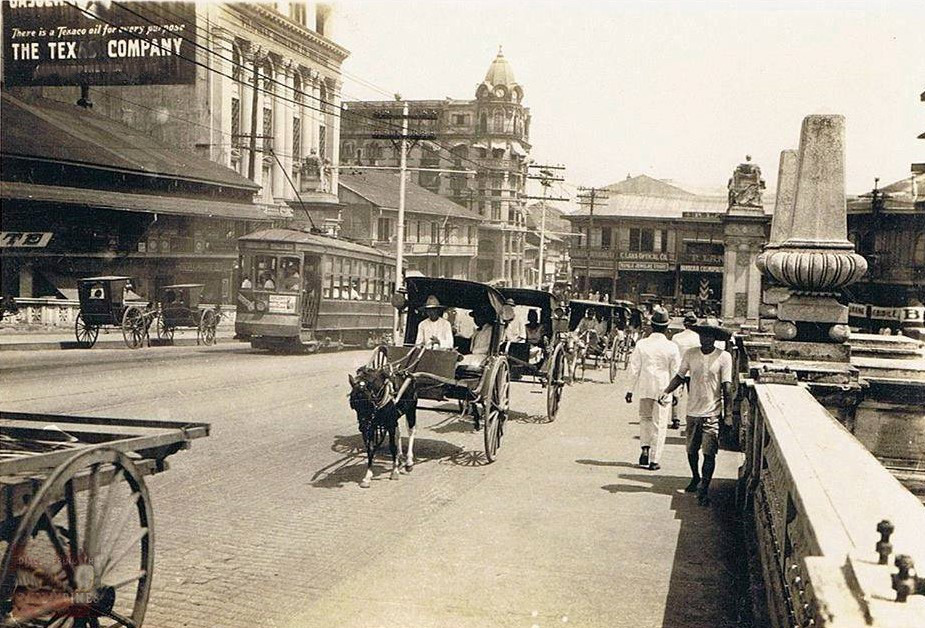

The brand new authorities additionally launched a brand new public schooling system, with English because the medium of instruction. Faculties just like the College of the Philippines (based in 1908) and Philippine Regular Faculty (now Philippine Regular College) have been established. The affect of American tradition, together with cinema, literature, and sports activities like basketball, turned widespread in Manila.
The arrival of American companies to Manila additionally led to a rise in employment alternatives. The introduction of contemporary banking system helped to facilitate financial actions in Manila. American rule efficiently reshaped Manila’s city panorama, governance, and social system. In the present day, most of the infrastructure and insurance policies from the American period proceed to affect Manila’s growth.
Submit-Conflict-Rebuilding and Independence
Following the tip of World Conflict II, Manila suffered intensive harm, with lots of its infrastructure, historic landmarks, and authorities buildings decreased to rubble. As a newly established Republic of Philippine took management of the nation in 1946, efforts to modernize and reconstruct the capital turned a precedence.
Submit-war years, the Philippine authorities underneath President Manuel Roxas, initiated restoration packages aimed toward restoring important providers and rebuilding the economic system. The reconstruction interval noticed rebuilding of presidency establishments, roads, and bridges. Additionally throughout this era, the USA supplied the newly unbiased republic with monetary support to assist the nation’s restoration efforts.
Manila underneath President Ferdinand Marcos and publish revolution
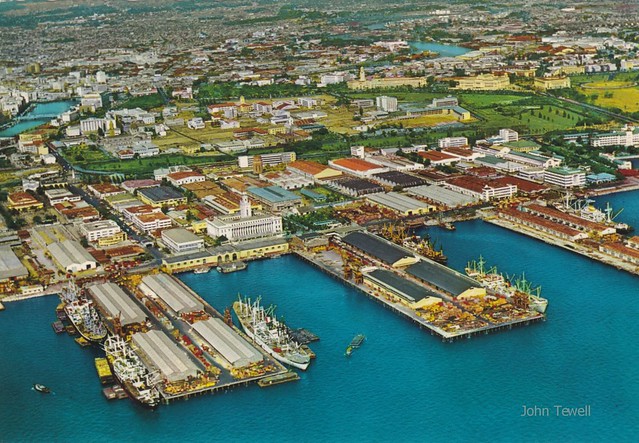
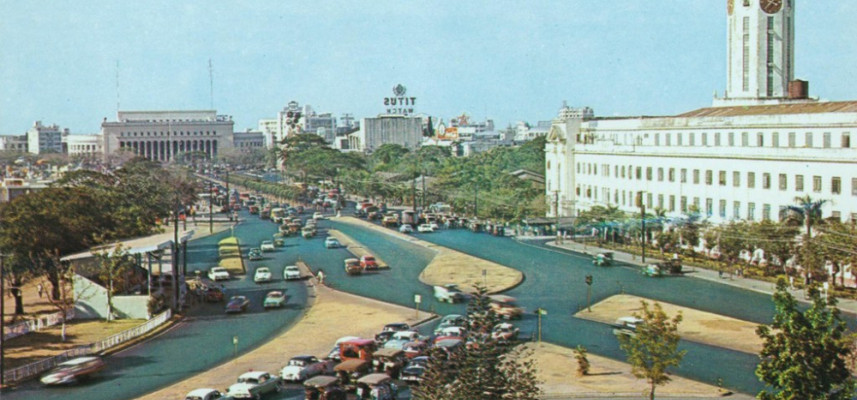


After few a long time, Manila skilled vital urbanization and financial development. The federal government efficiently constructed main infrastructures together with the development of highways, cultural facilities, and authorities complexes such because the Philippine Worldwide Conference Middle and the Cultural Middle of the Philippines. Nonetheless, fast urbanization additionally led to points equivalent to overpopulation, visitors congestion and the institution of casual settlements.
The post-1986 Folks Energy Revolution introduced in democratic reforms and a renewed deal with the town’s growth. Effort to decentralize governance allowed Metro Manila to develop as a regional financial hub. Underneath successive administrations, funding in transportation, actual property, and enterprise districts expanded. The development of main highways, the event of economic facilities like Makati and Bonifacio World Metropolis, and the growth of the railway system mirrored Manila’s steady modernization.
Manila within the twenty first Century
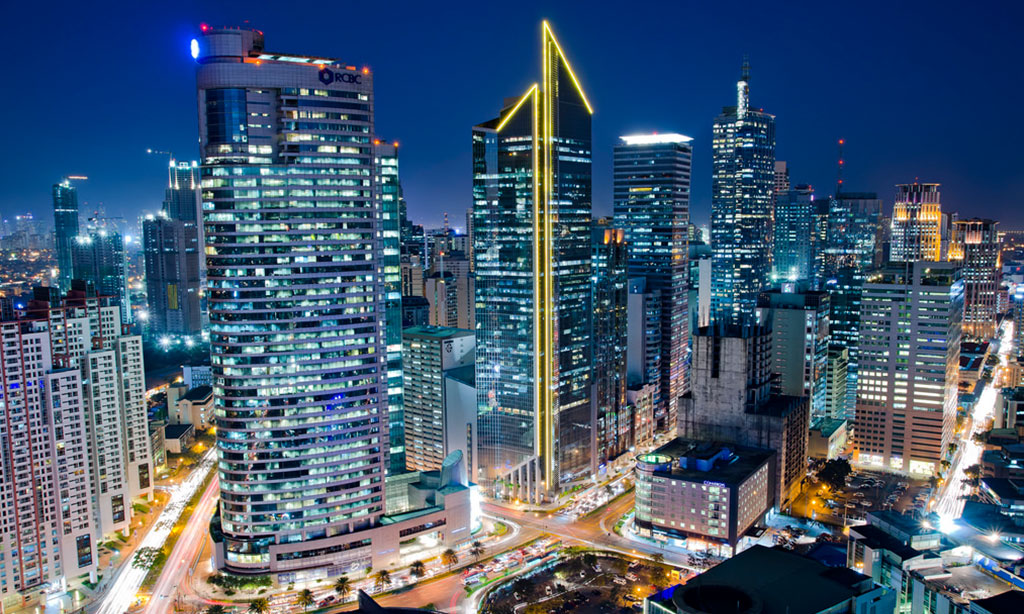
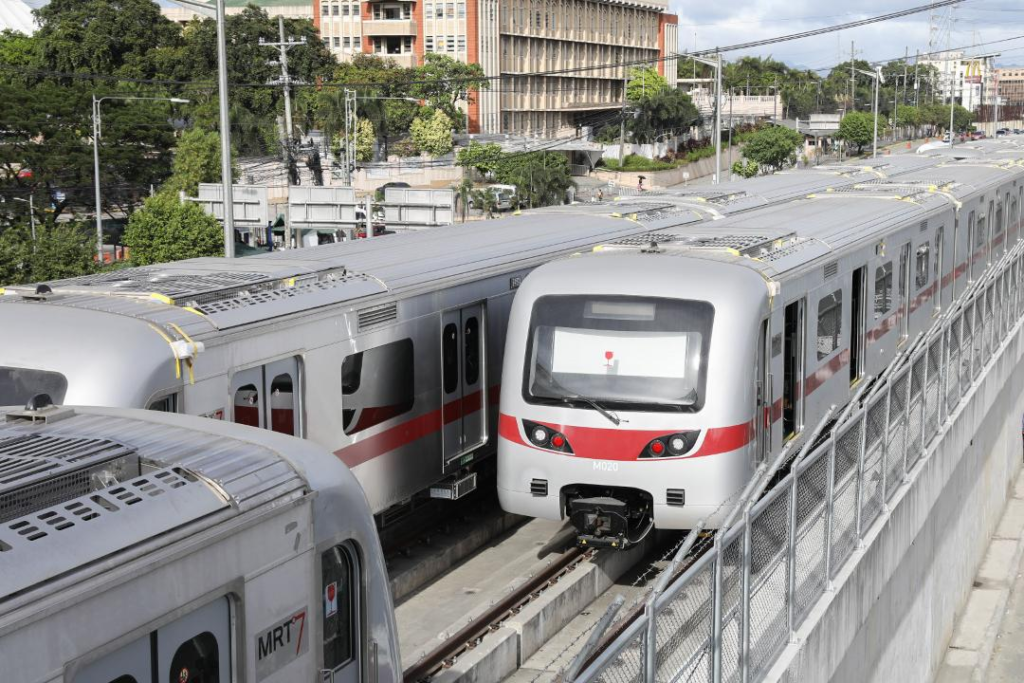
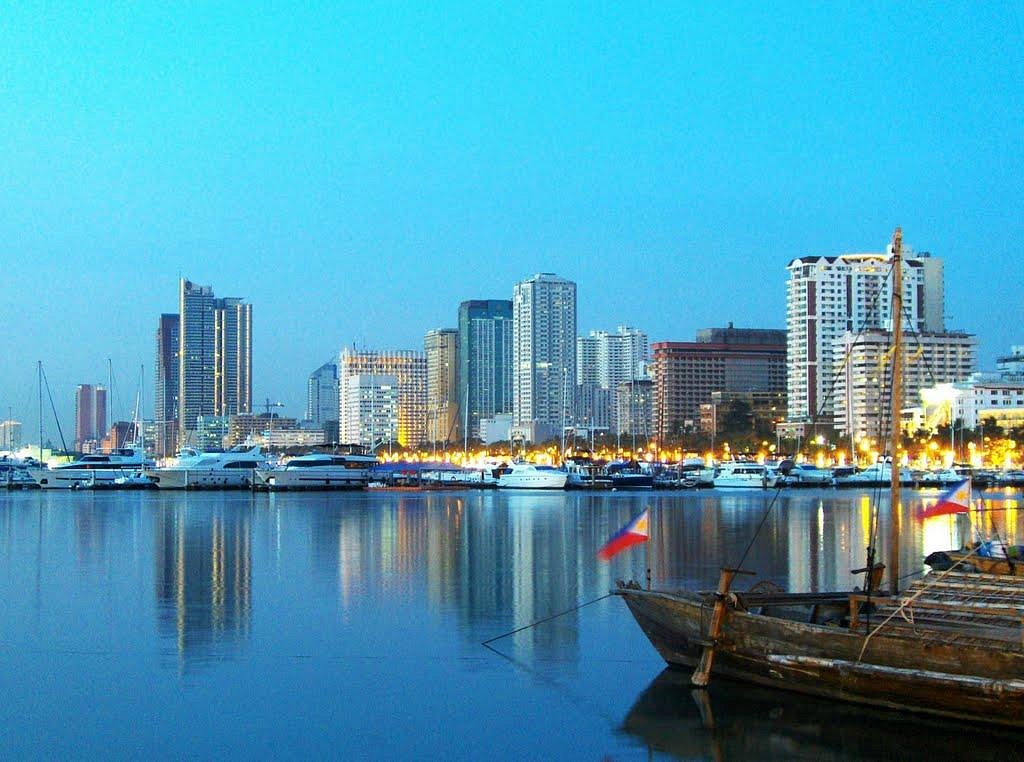



In recent times, Manila embraced sensible city planning and sustainability initiatives. Main authorities tasks within the twenty first century embody growth of mass transit methods and manila bay rehabilitation, with a serious purpose to deal with environmental challenges. The rise of enterprise course of outsourcing (BPO) industries and digital infrastructure has positioned Manila as a key participant within the international economic system.
In the present day, Manila stands as a dynamic metropolis, balancing historic preservation with modernization. Whereas challenges equivalent to visitors congestion, air pollution, and concrete poverty persist, ongoing growth tasks proceed to reshape the town. The Philippine Republic’s dedication to progress ensures that Manila stays an important financial, political, and cultural middle in Southeast Asia.
References
https://historytimelines.co/timeline/manila-philippines
Santos, J. (2022). Spanish Colonial Enclave Urbanism: Manila’s Intramuros and the way exclusion and waterway connectivity created the Binondo Manila Chinatown Buying and selling District. ResearchGate (on-line). Out there at: https://www.researchgate.web/publication/362807229_Spanish_Colonial_Enclave_Urbanism_Manila’s_Intramuros_and_how_exclusion_and_waterway_connectivity_created_the_Binondo_Manila_Chinatown_Trading_District
https://whc.unesco.org/fr/listesindicatives/6715/#
https://www.asianstudies.org/publications/eaa/archives/america-and-the-philippines/













Leave feedback about this